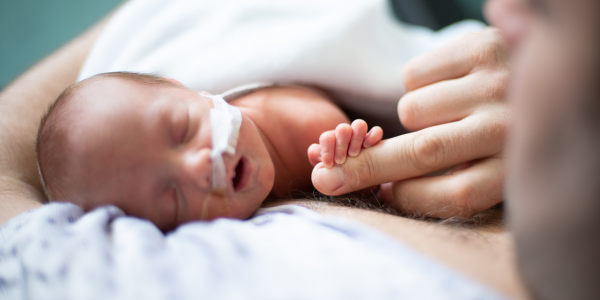
When a newborn enters the world, it should be a time filled with joy, hope, and anticipation of a bright future. However, for families whose infants are diagnosed with Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC), this moment of celebration can quickly turn into one of uncertainty, anxiety, and medical complexity. NEC is a daunting gastrointestinal condition that primarily affects premature infants but can also impact full-term babies and older children. It’s a condition that demands not only the utmost medical attention but also unwavering support and understanding from families.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to shed light on Necrotizing Enterocolitis – what it is, what causes it, how to recognize its symptoms, and the available treatment options. We’ll also introduce you to a beacon of hope in the form of the Eclipse XL1, an innovative medical device that’s changing the landscape of NEC treatment.
Section 1: What is NEC?
The Challenge of NEC
Necrotizing Enterocolitis, often referred to as NEC, is a complex and serious gastrointestinal disorder. It is characterized by inflammation and tissue damage within the intestines, particularly in the area where food and nutrients are absorbed. While NEC primarily affects premature infants, it is not limited to them and can occur in newborns and even older children. The onset of NEC can be abrupt and its consequences severe, making it a formidable challenge for both patients and their families.
The Complexity of Prematurity
A key factor contributing to NEC’s prevalence in premature infants is the underdeveloped nature of their digestive systems. Premature babies often face numerous health challenges, and their immature immune systems and gastrointestinal tracts make them more vulnerable to NEC. This vulnerability underscores the importance of understanding NEC within the context of prematurity.
The Cascade of Events
The development of NEC is a multi-step process, with the exact mechanisms still being studied by researchers. It often starts with damage to the intestinal lining, which can result from a combination of factors such as inadequate blood flow, infections, and feeding practices. This initial damage can trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses that further harm the intestinal tissue. Understanding this cascade is crucial for appreciating the complexity of NEC.
NEC: A Medical Emergency
NEC is not a condition that can be taken lightly. It is a medical emergency that requires swift and expert intervention. As parents and caregivers, being aware of the condition’s severity and urgency is essential. In the next sections, we’ll explore how to recognize the symptoms of NEC, what causes it, and the available treatment options, including a groundbreaking approach called the Eclipse XL1, which offers a glimmer of hope in the fight against NEC.
Section 2: Recognizing the Symptoms of NEC
Early Detection Saves Lives
Timely recognition of NEC symptoms can be the difference between life and death. NEC can progress rapidly, so understanding the signs is crucial for prompt medical intervention. If your infant exhibits any of the following symptoms, seek immediate medical attention:
- Feeding Difficulties: Infants with NEC may struggle with feeding, become lethargic during feedings, or refuse to eat altogether.
- Abdominal Swelling or Discoloration: A swollen and tender abdomen, often accompanied by a noticeable change in skin color, is a concerning sign.
- Bloody Stool: Blood in the stool, which may appear dark or maroon, can be a strong indicator of NEC.
- Irritability or Discomfort: NEC can cause discomfort and irritability in infants, leading to increased crying or fussiness.
- Temperature Instability: Fluctuations in body temperature, including hypothermia (low body temperature) or fever, can be associated with NEC.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early detection of NEC is essential because it allows for swift medical intervention. Diagnostic tests such as X-rays and blood tests help confirm the presence of the condition. If NEC is suspected, doctors may recommend ceasing oral feedings and providing nutrition through an intravenous (IV) line to give the intestines a chance to heal.
Partnering with Healthcare Providers
It’s essential for parents and caregivers to maintain open communication with healthcare providers. If you suspect NEC or notice any concerning symptoms in your infant, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Building a strong partnership with your healthcare team can significantly impact the outcome of NEC.
Section 3: What Causes NEC?
Unraveling the Complexity
While the precise causes of NEC are not fully understood, researchers believe that a combination of factors contributes to its development. Key factors include:
- Prematurity: Premature infants have underdeveloped immune systems and gastrointestinal tracts, making them more susceptible to NEC.
- Feeding Practices: The introduction of milk-based feeds, especially in premature infants, can be a potential trigger for NEC.
- Intestinal Ischemia: Inadequate blood flow to the intestines, often due to prematurity, can lead to tissue damage and NEC.
- Infections: Bacterial infections in the intestines can exacerbate inflammation and tissue damage.
- Inflammation: The body’s response to inflammation may play a role in the development and progression of NEC.
Preventive Measures
Understanding the potential risk factors for NEC can empower parents and healthcare providers to take preventive measures. For example, in the case of premature infants, gradual introduction of feeds and careful monitoring may reduce the risk. Ensuring a sterile environment and practicing strict hygiene in neonatal care units can also play a role in prevention.
Ongoing Research
Researchers continue to investigate the intricate details of NEC’s causes. Advances in medical science are uncovering new insights into how to prevent and manage this condition. Stay informed and engaged in discussions with your healthcare team to ensure the best care for your infant.
Section 4: Available Treatment Options
Addressing NEC Requires Comprehensive Care
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) is a complex condition that demands a multifaceted approach to treatment, tailored to the individual patient’s needs. While treatment plans may vary based on the severity of NEC, several common strategies are employed:
Stopping Oral Feedings
One of the initial steps in NEC treatment is discontinuing oral feedings. This allows the gastrointestinal tract to rest and heal. Nutritional support is then provided through an intravenous (IV) line to ensure the baby receives essential nutrients.
Antibiotics to Combat Infection
NEC often involves bacterial infections in the intestines. Doctors typically administer antibiotics to combat these infections and reduce the risk of sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
Monitoring and Imaging
Close monitoring and imaging, such as X-rays, are essential to track the progress of NEC and determine if surgical intervention is necessary. Frequent assessments help healthcare providers make informed decisions about the best course of action.
Surgery: A Last Resort
In severe cases of NEC, surgery may be required. Surgery aims to remove necrotic (dead) tissue, repair damaged intestines, and create an ostomy, where an opening in the abdomen diverts waste away from the damaged area. Surgical intervention is reserved for cases where medical treatments are ineffective or when the condition is life-threatening.
Section 5: Exploring New Horizons in NEC Research
Advancements in NEC Research
Researchers and medical professionals are continually striving to improve the understanding and treatment of Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Ongoing studies focus on various aspects of the condition:
Preventive Strategies
Efforts are being made to identify and implement preventive strategies, especially for premature infants who are at higher risk. Research explores the role of human milk, probiotics, and other interventions to reduce the incidence of NEC.
Early Detection Tools
The development of more sensitive diagnostic tools and biomarkers can aid in the early detection of NEC, enabling timely intervention and better outcomes.
Improving Non-Surgical Interventions
Medical treatments for NEC are continually refined, aiming to enhance their effectiveness and reduce the need for surgery.
A Commitment to Progress
As we conclude this exploration of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC), it is evident that NEC is a multifaceted and challenging condition. However, it is also a condition that brings together a community of dedicated healthcare professionals, researchers, and families, all committed to making a positive difference in the lives of those affected.
While the road ahead may be fraught with uncertainty, it is also paved with hope. Hope that ongoing research will reveal new insights into prevention and treatment. Hope that the dedication of medical experts will continue to improve outcomes for NEC patients. And hope that families facing NEC will find the support and resources they need to navigate this journey with strength and resilience.
Take Action for NEC Awareness
As you’ve embarked on this journey of understanding NEC, we encourage you to take action in raising awareness about this condition. Share your knowledge with others, support organizations dedicated to NEC research and support, and be an advocate for NEC awareness in your community.