Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) is a challenging and often life-altering condition that arises from extensive intestinal resection, leaving individuals with limited absorptive capacity in their digestive tract. For those affected, managing SBS has traditionally meant navigating a complex landscape of dietary restrictions, medications, and potential complications. However, a ray of hope has emerged in the form of the STEP/Bianchi procedure—a groundbreaking surgical intervention that promises to transform the lives of SBS patients.
A Paradigm Shift in SBS Management
The STEP (Serial Transverse Enteroplasty) procedure, also known as the Bianchi procedure, represents a paradigm shift in the treatment of Short Bowel Syndrome. Developed by Dr. Tom Jaksic and Dr. Paolo De Coppi, this innovative surgical approach offers the potential to increase the functional length of the remaining intestine, ultimately enhancing the body’s ability to absorb vital nutrients and fluids. It holds the promise of reducing dependence on parenteral nutrition and improving overall quality of life for SBS patients.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of the STEP/Bianchi procedure, exploring its principles, eligibility criteria, potential benefits, and what it means for individuals living with SBS and their families. It is a story of medical ingenuity and the pursuit of better outcomes for those facing the challenges of this complex condition.
1: Understanding Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS)
Deciphering Short Bowel Syndrome
To fully grasp the significance of the STEP/Bianchi procedure, it’s essential to begin by understanding the condition it seeks to address: Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS). SBS is a gastrointestinal disorder that occurs when a significant portion of the small intestine is surgically removed or non-functional due to disease. This condition can result from various factors, including congenital anomalies, surgical interventions for conditions like necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) or Crohn’s disease, and other underlying gastrointestinal disorders.
The Consequences of SBS
The hallmark of SBS is a reduced ability to absorb essential nutrients, vitamins, and fluids from food, leading to a range of debilitating symptoms. Individuals with SBS often experience:
- Chronic Diarrhea: The loss of functional intestine can result in frequent and watery stools, leading to dehydration and malnutrition.
- Weight Loss and Malnutrition: The inability to absorb adequate nutrients can lead to weight loss, malnutrition, and related complications.
- Dependence on Parenteral Nutrition: Many SBS patients rely on intravenous (IV) nutrition, known as parenteral nutrition, to meet their nutritional needs. While life-saving, this dependence can be burdensome and associated with potential complications.
The Challenges of SBS Management
Managing SBS has historically been a complex and demanding endeavor. It often involves:
- Specialized Diets: Individuals with SBS must adhere to carefully tailored diets that aim to maximize nutrient absorption and minimize digestive distress.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to control symptoms, promote intestinal motility, and manage complications.
- Parenteral Nutrition: For those with severe SBS, parenteral nutrition provides vital nutrients and hydration intravenously. However, its long-term use can be associated with complications, such as central line-associated bloodstream infections.
While these strategies can alleviate some of the challenges posed by SBS, they do not address the fundamental issue—the lack of sufficient functional intestine. The STEP/Bianchi procedure offers a potential solution by increasing the absorptive surface area of the intestine, potentially reducing the need for extensive medical interventions and enhancing overall quality of life for SBS patients.
2: The STEP/Bianchi Procedure Unveiled
A Surgical Innovation for SBS
The Serial Transverse Enteroplasty (STEP) procedure, also known as the Bianchi procedure, is a revolutionary surgical technique designed to provide hope and meaningful improvement in the lives of Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) patients. This groundbreaking approach involves a series of meticulous surgical steps aimed at increasing the functional length of the remaining small intestine, effectively enhancing the body’s capacity to absorb nutrients and fluids.
The Principle Behind STEP/Bianchi
The fundamental principle underlying the STEP/Bianchi procedure is the creation of a more extensive and convoluted intestinal configuration. During the surgery, the surgeon makes multiple transverse incisions along the length of the dilated bowel. These incisions are then folded, creating a zigzag pattern, and stitched together, effectively shortening the intestine’s lumen. This intricate process results in a significant increase in the absorptive surface area, allowing for improved nutrient and fluid absorption.
Potential Benefits of the STEP/Bianchi Procedure
The STEP/Bianchi procedure holds the promise of transformative benefits for individuals living with SBS. While outcomes can vary from person to person, potential advantages include:
- Reduced Dependency on Parenteral Nutrition: By enhancing intestinal absorption, the procedure may reduce the reliance on intravenous (IV) parenteral nutrition, improving the patient’s overall quality of life.
- Enhanced Nutritional Status: With improved nutrient absorption, SBS patients may experience weight gain and better nutritional status, addressing concerns of malnutrition and related complications.
- Improved Fluid Balance: Enhanced fluid absorption can alleviate issues of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, common in SBS patients.
- Decreased Frequency of Diarrhea: Many SBS patients experience chronic diarrhea, which can be mitigated through the improved functioning of the intestine after the procedure.
Eligibility and Considerations
While the STEP/Bianchi procedure offers considerable promise, not all SBS patients are eligible candidates. Surgical candidacy is determined based on several factors, including the length and condition of the remaining small intestine, overall health, and individual patient circumstances. A comprehensive evaluation by a skilled medical team is essential to assess eligibility and discuss potential risks and benefits.
As we proceed in this guide, we will explore the preoperative preparation, surgical process, postoperative care, and potential outcomes of the STEP/Bianchi procedure, shedding light on the transformative potential it holds for individuals living with SBS.
3: Preparing for the STEP/Bianchi Procedure
A Comprehensive Evaluation
Before undergoing the STEP/Bianchi procedure, individuals with Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS) undergo a thorough and individualized evaluation by a specialized medical team. This evaluation aims to assess the patient’s eligibility, overall health, and suitability for the surgery. Key components of the preoperative assessment include:
Assessment of Remaining Small Intestine
The length and condition of the remaining small intestine play a significant role in determining eligibility for the procedure. Extensive resection or severe damage to the intestine may impact the potential benefits of the surgery.
Nutritional and Metabolic Assessment
Nutritional status, metabolic health, and any existing malnutrition are carefully evaluated. Nutritional optimization may be necessary before surgery to enhance the patient’s readiness.
Individualized Treatment Plan
Based on the evaluation’s findings, the medical team develops an individualized treatment plan that considers the patient’s unique needs and circumstances. This plan outlines the surgical approach, anticipated outcomes, and postoperative care requirements.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Coping with the challenges of SBS can take a toll on an individual’s psychological and emotional well-being. Patients are provided with psychological support and counseling to address any emotional concerns and prepare mentally for the procedure.
Informed Decision-Making
Informed consent is a crucial aspect of the preoperative process. Patients and their families are provided with detailed information about the STEP/Bianchi procedure, including potential risks, benefits, and expected outcomes. This ensures that patients make informed decisions about their treatment.
4: The STEP/Bianchi Procedure: A Surgical Journey
The Day of Surgery
On the day of the STEP/Bianchi procedure, patients arrive at the hospital prepared for surgery. The surgical team ensures that all preoperative preparations are in place and that the patient is ready for the transformative surgery ahead.
Anesthesia and Surgical Incisions
The surgery begins with the administration of anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort and pain relief throughout the procedure. Surgical incisions are made as part of the process to access the small intestine.
STEP/Bianchi Procedure
The surgeon meticulously performs the STEP/Bianchi procedure, making transverse incisions along the length of the dilated bowel, folding and stitching them together. This intricate process creates the desired zigzag pattern and increases the absorptive surface area of the intestine.
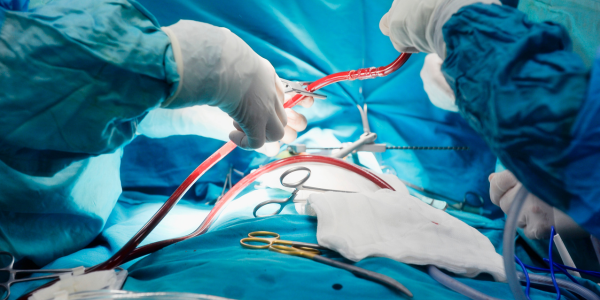
Postoperative Care and Monitoring
Following the surgery, patients are carefully monitored in the recovery area. Intravenous fluids and nutrition may be provided initially, gradually transitioning to oral intake as the intestine heals and adapts.
Potential Complications
Like any surgical procedure, the STEP/Bianchi procedure carries potential risks and complications, which are thoroughly discussed with the patient during the preoperative phase. Close postoperative monitoring helps detect and address any complications promptly.
Expected Outcomes and Postoperative Recovery
As the patient recovers from surgery, the medical team closely monitors their progress. The goal is to optimize nutritional intake and intestinal function while reducing dependence on parenteral nutrition. The expected outcomes can vary, with some patients experiencing significant improvements in their quality of life.
In the upcoming sections of this guide, we will explore postoperative care, potential outcomes, and the transformative impact of the STEP/Bianchi procedure on the lives of individuals living with Short Bowel Syndrome.
A New Dawn for SBS Patients with the STEP/Bianchi Procedure
As we conclude this journey through the revolutionary STEP/Bianchi procedure, it is evident that hope shines brightly for individuals living with Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS). This innovative surgical approach represents a significant stride forward in SBS management, promising improved quality of life, reduced reliance on parenteral nutrition, and a newfound sense of normalcy for those who have long grappled with the challenges of this complex condition.
Embracing Transformation
The STEP/Bianchi procedure is more than just a surgical intervention; it is a beacon of hope and transformation. By enhancing the absorptive capacity of the remaining small intestine, this procedure holds the potential to alleviate chronic symptoms, reduce complications, and empower SBS patients to regain control of their lives.
Taking the Next Steps
If you or a loved one are living with SBS and considering the STEP/Bianchi procedure, the next step is to embark on a journey of exploration and consultation. Reach out to specialized medical centers and expert healthcare providers to initiate the evaluation process and discuss the potential benefits of this groundbreaking surgery.